- Name: j0.dev.local
- Ip Address: 192.168.10.41
- Network Interface: em0
Tuesday, December 11, 2012
How to create Jail in FreeBSD
Operating system virtualization is the most effective way to utilize your system resources, jails let you setup isolated mini-systems. Jails are explains well in handbook however, from practical standpoint of view, the presented material is incomplete. Here we will setup few scrips that follow handbook's 'Application of Jails' article and enhance with few missing features. Let note preliminary requirements:
Monday, December 3, 2012
How to Send Mail in Python
There are several use cases how you can send an email message using Python:
- Plain Mail: an email message with plain text or html content.
- Mail with Attachment: an email message with attached document.
- Alternative Mail Views: you provide a convenient way to email recipients to view your message in plain text or html with optional rich content including images, etc.
Labels:
algorithms
,
python
,
wheezy.core
Wednesday, November 28, 2012
How to ship eggs with pyo files only in Python
There is sometimes a need to ship python egg distribution with pyo files only. There is confusion using bdist_egg command since it doesn't have any options to do that; instead, you can instruct install_lib command. Here is what you need in setup.cfg file:
[install_lib] compile = 0 optimize = 2 [bdist_egg] exclude-source-files = 1Issue the following command to build egg.
python setup.py -q bdist_eggNote, the egg file has only python byte code optimized module files (look at dist directory). You can read about compiled modules here.
Labels:
python
,
setuptools
,
tricks
Tuesday, November 20, 2012
Python Web Frameworks Excessive Complexity
Cyclomatic (or conditional) complexity is a metric used to indicate the complexity of a source code. In this post we will take a look at web frameworks source code and estimate excessive complexity, something that is beyond recommended level of 10 (threshold that points to the fact the source code is too complex and refactoring is suggested). Here is a list of web frameworks examined:
- bottle
- cherrypy
- circuits
- django
- falcon
- flask
- pyramid
- pysi
- tornado
- turbogears
- web.py
- web2py
- webapp2
- wheezy.web
hg clone https://bitbucket.org/akorn/helloworld cd helloworld/04-pep8 && make env upThe make file has a target for mccabe metric, so issue make mccabe.
Thursday, November 15, 2012
Lazy Attribute in Python
A lazy attribute is an attribute that is calculated on demand and only once. Here we will see how you can use lazy attribute in your Python class. Setup environment before you proceed:
$ virtualenv env $ env/bin/pip install wheezy.coreLet assume we need an attribute that is display name of some person Place the following code snippet into some file and run it:
from wheezy.core.descriptors import attribute
class Person(object):
def __init__(self, first_name, last_name):
self.first_name = first_name
self.last_name = last_name
self.calls_count = 0
@attribute
def display_name(self):
self.calls_count += 1
return '%s %s' % (self.first_name, self.last_name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = Person('John', 'Smith')
print(p.display_name)
print(p.display_name)
assert 1 == p.calls_count
Notice display_name function is decorated with @attribute. The first call promotes function to attribute with the same name. The source is here.
Labels:
algorithms
,
python
,
wheezy.core
Thursday, November 8, 2012
Duck Typing Assert in Python
People who come from strongly typed languages that offer interfaces often are confused by lack of one in Python. Python, being dynamic typing programming language, follows duck typing principal. Here we will see how programmer can assert duck typing between two Python classes. Setup environment before proceed:
$ virtualenv env $ env/bin/pip install wheezy.coreLet play a bit with duck test `looks like`. Place the following code snippet into file `test.py`:
from wheezy.core.introspection import looks
class IFoo(object):
def foo(self):
pass
class Foo(object):
def bar(self):
pass
assert looks(Foo).like(IFoo)
Labels:
algorithms
,
python
,
wheezy.core
Friday, November 2, 2012
How to generate account number?
Requirements for `account number` generator:
- Issue pseudo random consistent number (must be unique for dozen millions of records)
- Easy check validity (without a need to make a database call)
$ virtualenv env $ env/bin/easy_install wheezy.core $ env/bin/pythonLet play a bit how numbers are generated (notice, the function is reversal and consistent, all numbers are unique, no collision):
>>> from wheezy.core.feistel import make_feistel_number >>> from wheezy.core.feistel import sample_f >>> feistel_number = make_feistel_number(sample_f) >>> feistel_number(1) 573852158 >>> feistel_number(2) 1788827948 >>> feistel_number(1788827948) 2We will use Luhn algorithm to generate a single digit checksum. This algorithm is taken as basis for the module available in wheezy.core package.
>>> from wheezy.core.luhn import luhn_checksum >>> luhn_checksum(123456789) 7There are two more useful functions to sign a number and also check it validity:
>>> from wheezy.core.luhn import luhn_sign >>> from wheezy.core.luhn import is_luhn_valid >>> luhn_sign(123456789) 1234567897 >>> is_luhn_valid(1234567897) True >>> is_luhn_valid(34518893) FalseNow let just make account number looking nice (pad with zeros, prefix with something meaningful, etc):
>>> account_number = lambda n: 'Z%011d' % luhn_sign( \ ... feistel_number(n)) >>> account_number(1) 'Z05738521581' >>> account_number(2) 'Z17888279480' >>> account_number(3) 'Z07395350007'Per discussion in python mail list, there was discovered alternative, human readable representation of the same number:
>>> from base64 import b32encode >>> human_format = lambda n: 'Z%s-%s' % (b32encode( \ ... chr((n >> 24) & 255) + \ ... chr((n >> 16) & 255))[:4], \ ... b32encode(chr((n >> 8) & 255) + \ ... chr(n & 255))[:4]) >>> human_format(5738521581) 'ZKYFA-4PWQ' >>> human_format(17888279480) 'ZFI4Q-PO4A' >>> human_format(7395350007) 'ZXDGA-CX3Q'Side by side:
Z05738521581 = ZKYFA-4PWQ Z17888279480 = ZFI4Q-PO4A Z07395350007 = ZXDGA-CX3QYes, it optimized for speed, you must provide your own `sample_f` implementation for security reasons. Source code available here.
Labels:
algorithms
,
python
,
wheezy.core
Friday, October 26, 2012
wheezy web: introduction
The key of success for any medium to high complexity system is in separation of domain concerns. Given that choice in architectural design for web framework, the development activities are split by distinct, non-dependent parts. The wheezy.web is a lightweight WSGI web framework and serves a glue purpose between various other packages developed under wheezy.* umbrella in loosely coupled way, it combines things essential for web application developer (presentation slides are here):
- routing - simple extensible mapping between URL patterns (as plain simple strings, curly expressions or regular expressions) to a handler; the mapping can include other mappings and constructed dynamically; reverse path by name
- domain model update from request input; validation
- transparent validation errors integration in HTML widgets
- authentication/authorization
- i18n (gettext)
- middlewares, response transforms, cookies, etc
- content caching, HTTP cache policy and cache profiles + cache dependency
- functional testing
- template engine agnostic, however brings wheezy.template. It offers HTML widgets for various template engines to make your code more readable and consistent (via template preprocessing to generate an optimal markup for given template engine)
- integration with pycrypto, lxml, python-memcached and pylibmc; the wheezy.captcha library is based on PIL
- documentation per package, tutorial, examples, demo
- Python 2.4 - 3.3+ ready
Labels:
python
,
wheezy.web
Thursday, October 25, 2012
Python Web Caching Benchmark
Content caching is the most effective type of cache. This way your web handler is not executed to determine a valid response to user, instead one returned from cache. Since the operation is that simple, it should be the maximum possible speed your `real world` application capable to provide. There are several use cases when content caching is applicable:
- Site: the site content is changed rarely. The best case scenario is nginx+wsgi caching facilities, see more here.
- Handler: the site content caching policy vary, there are only few handlers were content caching is applicable.
- Managed (semi-real time): the site is dynamic, it is not permissible to cache a given output unless there is a way to invalidate content since some data changed, e.g. item price, new message arrived, etc. Read more here or give it a try.
- django 1.4.2
- flask 0.9
- wheezy.web 0.1.307
Tuesday, October 23, 2012
Python Templates Benchmark
Python template engines offer high reusability of markup code and the following features are used by content developers most of the time:
- Includes: useful to incorporate some snippets of content that in most cases are common to the site, e.g. footer, scripts, styles, etc.
- Extends: useful to define a master layout for the majority of the site content with placeholders, e.g. sidebar, horizontal menu, content, etc. The content developers extend the master layout by substituting available placeholders.
- Widgets: usually small snippets of highly reusable markup, e.g. list item, button, etc. The content developers use widgets to increase readability and enforce consistency of design.
Labels:
benchmark
,
django
,
python
,
wheezy.template
Thursday, October 18, 2012
Python Web Frameworks PEP8 Consistency
The code is read much more often than it is written. The PEP8 guidelines are intended to improve the readability of code. Readability counts, no doubt, but readability consistency is important, it is equally important to know when to be inconsistent. The report below makes excuse for the following:
E501 line too long (> 79 characters) E231 missing whitespace after ',:' W291 trailing whitespace W293 blank line contains whitespaceIn this post we will take a look at web frameworks source code readability. The ratio between a web framework total python source lines to PEP8 errors found represents PEP8 error rate in respectful framework:
- bottle
- cherrypy
- circuits
- django
- falcon
- flask
- pyramid
- pysi
- tornado
- turbogears
- web.py
- web2py
- webapp2
- wheezy.web
hg clone https://bitbucket.org/akorn/helloworld cd helloworld/04-pep8 && make env upThe make file has a target for each metric, so in order to gather pep8 count issue make pep8, or make count to count total lines.
Monday, October 15, 2012
Python Web Reverse URLs Benchmark
How fast python web frameworks reverse urls? While routing is a mapping of incoming request to a handler, url reverse function is designed to build urls for those handlers. A web page may have a number of urls from few dozen to hundreds... all related to your web site (e.g. links between related pages, tag cloud, most viewed posts, etc). A typical web application usually has deal with the following reverse url use cases:
- Static: the URL path is fixed and never changes, e.g. https://bitbucket.org/explore.
- Merge: the URL path is constructed dynamically, some information is taken from URL. A `user page` shows repositories. In this case a list of user repositories will be constructed as merge of information that came from URL (user name) and repository name.
- Route: the URL path is constructed dynamically, all information can be taken from URL. A `repository page` displays a number of features: downloads, source, etc. Those links include current route information (user name and repository name).
apt-get install make python-dev python-virtualenv \
mercurial unzip
The source code is hosted on bitbucket, let clone it into some directory and setup virtual environment (this will download all necessary package dependencies per framework listed above).
hg clone https://bitbucket.org/akorn/helloworld cd helloworld/03-urls && make envOnce environment is ready we can run benchmarks:
env/bin/python benchmarks.py
Tuesday, October 9, 2012
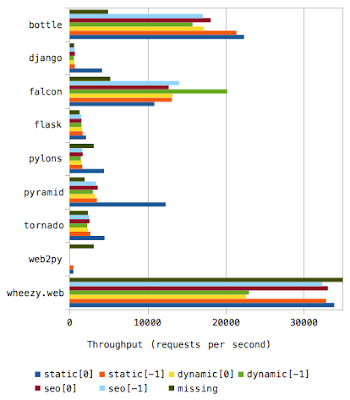
Python Web Routing Benchmark
How fast python web framework process routing (some calls this URL dispatch)? A typical web application usually has the following routes:
- Static: the URL path is fixed and never changes, e.g. https://bitbucket.org/explore.
- Dynamic: the URL path is constructed dynamically and can include semantic information, e.g. https://bitbucket.org/jsmith/dotfiles/downloads, in this case jsmith is user, dotfiles a name of source repository, downloads - feature.
- SEO: localization and internationalization is sort of must have for modern web applications, can combine two above.
- Missing: that always happen, url changed and resource is not available anymore. What is impact of handing a non-existing path?
- bottle 0.11.6
- django 1.6
- falcon 0.1.7
- flask 0.10.1
- pylons 1.0.1
- pyramid 1.5a2
- tornado 3.1.1
- web2py 2.2.1
- wheezy.web 0.1.373
apt-get install make python-dev python-virtualenv \
mercurial unzip
The source code is hosted on bitbucket, let clone it into some directory and setup virtual environment (this will download all necessary package dependencies per framework listed above).
hg clone https://bitbucket.org/akorn/helloworld cd helloworld/02-routing && make envOnce environment is ready we can run benchmarks:
env/bin/python benchmarks.py
Thursday, October 4, 2012
apt-get: update only required translations
apt Acquire::Languages can be set to declare which translations you want downloading. The variable "environment" specifies that apt should check $LC_MESSAGES. Here we go:
# eliminate any lists you might have
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/
# set languages you need
echo 'Acquire::Languages { "environment"; "en"; };' > \
/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/99lang
# update lists
apt-get update
If you need just English, it is okay just remove apt lists.
Tuesday, September 18, 2012
Python Fastest Web Framework
What is the fastest web framework for Python? In this post we will examine a trivial 'Hello World!'. See also:
- Performance Benchmarks
- Code Quality
- Template Engines
- bobo 1.0.0
- bottle 0.11.6
- cherrypy 3.2.4
- circuits 2.1.0
- django 1.5.1
- flask 0.9
- pyramid 1.4
- tornado 3.0.1
- turbogears 2.2.0
- web.py 0.37
- web2py 2.1.1
- wheezy.web 0.1.365
apt-get install make python-dev python-virtualenv \
mercurial unzip
# Up TCP connection limits
sysctl net.core.somaxconn=2048
sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog=2048
The source code is hosted on bitbucket, let clone it into some directory and setup virtual environment (this will download all necessary package dependencies per framework listed above).
hg clone https://bitbucket.org/akorn/helloworld cd helloworld/01-welcome && make envThe make file has a target for each framework and runs particular example in uWSGI, e.g. in order to run django application just issue make django.
Wednesday, August 22, 2012
How to restore vim screen when exiting
When you exit vim it does not restore the terminal screen (particularly in FreeBSD), here is how to fix that (file ~/.vimrc):
" Restore terminal screen when exiting Vim if &term =~ "xterm" let &t_ti = "\<Esc>[?47h" let &t_te = "\<Esc>[?47l" endif
Labels:
freebsd
,
tricks
,
troubleshooting
,
vim
Sunday, August 19, 2012
Rebuilding World and Kernel on FreeBSD
Building the world and kernel on FreeBSD is just few steps procedure. The Handbook explains everything in great details. Here is short version.
Keep FreeBSD up to date with csup
csup is a simple tool to keep you FreeBSD source and/or ports collection up to date (rewrite of CSVup in C). There are a number of mirrors around the world hosting the source code and you need to select one that is closest to your location. Use a tool like traceroute to find a one that responds best (shortest path, low delays).
Labels:
freebsd
FreeBSD Binary/Security Updates
freebsd-update is a tool to fetch and update binary security patches for official releases. e.g. FreeBSD 9.0-RELEASE. Once you made fresh OS install this is the way to update your system quickly.
freebsd-update fetch freebsd-update installNote, this tool doesn't work if you build world/kernel from source.
Saturday, August 18, 2012
FreeBSD make.conf example
make.conf stores system-wide build settings that apply each time you run make. Copy example:
cp /usr/share/examples/etc/make.conf /etcCompile the source code specific to your CPU:
CPUTYPE?=nativeIt is recommended uncomment the following: CFLAGS, CXXFLAGS, COPTFLAGS.
# 2 jobs per CPU MAKE_JOBS_NUMBER=4 # KNOBS -- A list of popular knobs and their descriptions # http://svn.freebsd.org/ports/head/KNOBS?view=markup # Do not to compile X11 support WITHOUT_X11= # Include python support, e.g. in Vim WITH_PYTHON= # Do not build and install the doc, examples, mans WITHOUT_EXAMPLES= WITHOUT_DOCS= NOPORTDOCS= NOPORTEXAMPLES= NO_INSTALL_MANPAGES=
How to setup HTTP Proxy in FreeBSD
The HTTP proxy is set through environment variable HTTP_PROXY. Environment variables can be controlled during user login. Assuming the proxy is proxy.somewhere.net:3128 ensure the following in /etc/login.conf:
:setenv=HTTP_PROXY=http\c//proxy.somewhere.net\c3128:\Update login capability database:
cap_mkdb /etc/login.confRe-login and ensure it is properly set:
env | grep HTTP_PROXY
How to SU with no password in FreeBSD
You can allow user to switch to root account without password. You need to add user to wheel group:
pw usermod john -G wheeland change pam policy (file /etc/pam.d/su):
#auth requisite pam_group.so no_warn group=wheel root_only fail_safe ruser auth sufficient pam_group.so no_warn group=wheel root_only fail_safe ruserIt is necessary to re-login so new group membership take place. Issue the following command to check user group:
$ id uid=1001(john) gid=1001(john) groups=1001(john),0(wheel)
FreeBSD C Shell Tricks
C shell is default shell for root account in FreeBSD. You can control settings through the following configuration files:
~/.cshrc - user specific settings
/etc/csh.cshrc - global settings
Color Prompt: display hostname in red color for shell prompt (read more here):
~/.cshrc - user specific settings
/etc/csh.cshrc - global settings
Color Prompt: display hostname in red color for shell prompt (read more here):
set prompt="%{\033[1;31m%}%m %{\33[34m%}%. %{\033[0m%}%# "
set promptchars = "%#"
or if above doesn't work:
alias setprompt 'set prompt="%{\033[1;31m%}`/bin/hostname -s` %{\33[34m%}$cwd:t %{\033[0m%}# "'
setprompt
alias cd 'chdir \!* && setprompt'
List directories in color:
alias ls ls -GDel Key In Terminal:
bindkey ^[[3~ delete-char
FreeBSD Bourne Shell Tricks
Bourne shell is default shell for user account in FreeBSD. You can control settings through the following configuration files:
~/.shrc - user specific settings
/etc/profile - global settings
Color Prompt: display hostname in green color for shell prompt (read more here):
~/.shrc - user specific settings
/etc/profile - global settings
Color Prompt: display hostname in green color for shell prompt (read more here):
# vi ^[: ctrl+v and then Esc #PS1="^[[32m$^[[0m " PS1="^[[1;32m`whoami`@\h ^[[34m\W ^[[0m$ "List directories in color:
alias ls='ls -G'Color case insensitive grep:
export GREP_OPTIONS='-i --color=auto'
FreeBSD Virtual Machine Loader Settings
It is recommended to lower kernel internal timer rate and delay before auto booting:
Add the following to /boot/loader.conf:
kern.hz=100 # The kernel interval timer rate autoboot_delay=3 # Delay in seconds before autobootingRead more here.
Labels:
freebsd
,
kvm
,
virtualbox
Thursday, July 19, 2012
Python Fastest Template Engine
What is the fastest template system for Python? See also:
- Comprehensive benchmarks for various template include, extends and widget directives are here.
- bottle 0.12.8
- chameleon 2.22
- cheetah 2.4.4
- django 1.8
- jinja2 2.7.3
- mako 1.0.1
- durusworks qpy 1.2
- spitfire 0.7.15
- tenjin 1.1.1
- tornado 4.1
- web2py 2.0.9
- wheezy.template 0.1.159
virtualenv env env/bin/easy_install -O2 bottle chameleon cheetah django \ jinja2 mako tenjin webext tornado wheezy.html \ wheezy.templateDownload bigtable.py test:
wget https://bitbucket.org/akorn/wheezy.template/raw/tip/demos/bigtable/bigtable.pyAnd run it:
env/bin/python bigtable.py
Labels:
benchmark
,
django
,
python
,
wheezy.template
Thursday, June 21, 2012
Troubleshooting slapd error: too many open files
Debian testing comes with openldap (slapd package) version 2.4.28. I noticed that ldap clients start receiving error and cannot contact ldap service any more. While the slapd daemon was running I found a number of errors in syslog (file /var/log/syslog):
... ldap1 slapd[4894]: SASL [conn=1611] Failure: GSSAPI Error: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information (Too many open files) ... ldap1 slapd[4894]: warning: cannot open /etc/hosts.allow: Too many open files ... ldap1 slapd[4894]: warning: cannot open /etc/hosts.deny: Too many open files ... ldap1 slapd[4894]: SASL [conn=1611] Failure: GSSAPI Error: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information (Too many open files)Take a look at slapd process max open files soft limit:
cat /proc/`pidof slapd`/limitsCheck number of files open by slapd process:
pidof slapd | xargs lsof -a -p | wc -lThe slapd process must not exceed max open files soft limit. Take a look at files opened by slapd process:
pidof slapd | xargs lsof -a -p | tailHere is a sample output that shows there are a number of deleted files... actually one file /var/tmp/ldap_103.
slapd 4894 openldap 117u REG 0,197 3371 705975 /var/tmp/ldap_103 (deleted) slapd 4894 openldap 118u REG 0,197 3371 705975 /var/tmp/ldap_103 (deleted) slapd 4894 openldap 119u REG 0,197 3371 705975 /var/tmp/ldap_103 (deleted)There is definitely a bug in slapd that cause max open files limit exceed.
Recycle Process
We can write a script that does a check and restart daemon if it reaches certain limit (file /usr/local/sbin/slapd-restart).
#!/bin/sh
# Restart slapd daemon if it has open more than 512 files
if [ `pidof slapd | xargs lsof -a -p | wc -l` -gt 512 ]
then
/etc/init.d/slapd restart
fi
Let cron run this script hourly:
ln -s /usr/local/sbin/slapd-restart \ /etc/cron.hourly/slapd-restartIf slapd process exceed max open files soft limit too quickly consider schedule cron job more frequently.
Mount /var/tmp in tmpfs
While slapd process creates small files in /var/tmp quite quickly I found reasonable to mount it with tmpfs (file /etc/fstab):tmpfs /var/tmp tmpfs noatime,nodev,noexec,nosuid,size=1M 0 0Restart slapd daemon so changes take place:
/etc/init.d/slapd stop # Ensure the /var/tmp is empty rm /var/tmp/ldap_103 mount /var/tmp /etc/init.d/slapd start # Ensure the /var/tmp mounted df -h | grep /var/tmpEnsure the /var/tmp mounted:
tmpfs 1.0M 4.0K 1020K 1% /var/tmpRegularly take a look a /var/log/syslog if there are any errors reported.
Labels:
debian
,
kerberos
,
ldap
,
security
,
troubleshooting
Tuesday, June 12, 2012
How to Convert FLAC to MP3 in a Batch
Converting flac to mp3 package pre-requirements are the same as published in another post (How to Convert APE+CUE to MP3). So I will add what is necessary. You will need flac package.
apt-get -y install flacHere is a script that does the rest (file flac-mp3.sh):
#!/bin/bash
for f in *.flac
do
metaflac --export-tags-to=- "$f" | \
sed 's/=\(.*\)/="\1"/' | \
sed 's/\(.*\)=/\L&/' > tags.sh
. ./tags.sh
rm ./tags.sh
out_dir="mp3/$artist/$album"
if [ ! -d "$out_dir" ]; then
mkdir -p "$out_dir"
fi
flac -cd "$f" | lame -h - -v --preset cd \
--tt "$title" \
--tn "$tracknumber" \
--tg "$genre" \
--ty "$date" \
--ta "$artist" \
--tl "$album" \
--add-id3v2 \
"$out_dir/${f%.*}.mp3"
done
Drop that file into a directory that has flac files. Run the script and in few minutes you will get a mp3 directory with your mp3 tracks folded by artist/album.
Thursday, June 7, 2012
Gnome Keyring: Location
Gnome keyring can automatically unlock passwords stored in the keyring. Gnome keyring include the following components: pkcs11, gpg, secrets, ssh. You can take a look at various passwords and keys stored by running (Alt + F2) seahorse.
Various keyrings are unlocked during user login. You can control which one by reviewing gnome startup application preferences, take a look by running gnome-session-properties.
The problem I faced with was related to the fact that keyring daemon place it runtime data into $HOME/.cache/keyring-* directory and over time there are quite a lot of them there. So while these data are session specific I would think it is most appropriate to store this information somewhere in temporary storage (e.g. /tmp) so it cleaned up. Fortunately you can define environment variable $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR that points to /tmp and that get it solved.
Various keyrings are unlocked during user login. You can control which one by reviewing gnome startup application preferences, take a look by running gnome-session-properties.
The problem I faced with was related to the fact that keyring daemon place it runtime data into $HOME/.cache/keyring-* directory and over time there are quite a lot of them there. So while these data are session specific I would think it is most appropriate to store this information somewhere in temporary storage (e.g. /tmp) so it cleaned up. Fortunately you can define environment variable $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR that points to /tmp and that get it solved.
echo "export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/tmp" > \
/etc/profile.d/gnome-keyring.sh
The keyring daemon properly manage file permission so it owned and readable by user only. Once you reboot your computer the system level profile will setup environment variable for you so keyring cache will be created out there.
Labels:
debian
,
gnome
,
security
,
troubleshooting
Friday, June 1, 2012
Debian APC UPS client-server monitoring
Apcupsd is a UPS control system that permits orderly shutdown of your computer in the event of a power failure. We will take a look at NIS (Network Information Server) server and client configuration (this is the case when a single UPS powers several computers).
Server
NIS (Network Information Server) mode allows communication between different hosts. Only one of those hosts, the server, needs to talk to the UPS directly.-
Ensure device is connected and recognized. In most cases your UPS is connected to server via USB cable. In Linux you can check this by listing USB devices (provided by usbhid driver):
deby1:~# ls /dev/usb/ hiddev0
If your device is no connected, most likely, you will get a message like this:ls: cannot access /dev/usb/: No such file or directory
Note, in our case the UPS device is available at /dev/usb/hiddev0. - Install UPS monitoring software. Apcupsd is a software designed to control APC UPS devices, let get it installed:
apt-get install apcupsd
- Configure apcupsd. Ensure the following settings (file /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.conf):
UPSCABLE usb UPSTYPE usb DEVICE /dev/usb/hiddev0 NISIP 0.0.0.0
Let apcupsd daemon know it is configured (file /etc/default/apcupsd):ISCONFIGURED=yes
- Start apcupsd service:
/etc/init.d/apcupsd start
Check UPS status:apcaccess status <server name>
Take a look at any errors reported (file /var/log/apcupsd.events):... apcupsd 3.14.10 (...) debian startup succeeded
Client
The client computer will communicate with server via network.- Install UPS monitoring software.
apt-get install apcupsd
- Configure apcupsd. Ensure the following settings (file /etc/apcupsd/apcupsd.conf):
UPSCABLE ether UPSTYPE net #DEVICE hostname:port DEVICE deby1.dev.local:3551 NETSERVER off
Let apcupsd daemon know it is configured (file /etc/default/apcupsd):ISCONFIGURED=yes
- Start apcupsd service:
/etc/init.d/apcupsd start
Notifications
You are able receive a number of notification events, e.g. power failure, etc (see a complete list of events here). By default apcupsd calls script located at /etc/apcupsd/apccontrol. This script echo some events to user console, as well as shuts down host per doshutdown event. You can easily extend this script to email you events. Here is the script (file /usr/local/sbin/notify.sh):
#!/bin/sh
domain=`hostname -d`
mail=root@$domain
msg=Test
if [ ! -z "$2" ]; then
mail=$1; msg=$2
if ! echo $mail | grep -q "$domain"; then
mail=$mail@$domain
fi
else
if [ ! -z "$1" ]; then msg=$1; fi
fi
# strip whitespace at the end of message
msg=`echo "$msg" | sed 's/ *$//g'`
echo $msg | mail -s "$msg" $mail
echo $msg | wall
Ensure the following in apc event handler (file /etc/apcupsd/apccontrol):
#WALL=wall WALL="xargs -0 notify.sh ups@dev.local"This will email all events handled by apccontrol to ups@dev.local.
Friday, March 23, 2012
How to install PostgreSQL in Debian
PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system.
Server
Installation in Debian is straight forward:apt-get install postgresqlThe installation adds a linux administrative user account postgres. You will need to set password (consider take a look how to generate a strong password here):
passwd postgresThere is also user postgres in database. The passwords for both should be different. Let change securely password for database user postgres (you will need this password to connect to database):
psql01:~# su - postgres psql01:~$ psql psql (9.1.3) Type "help" for help. postgres=# \password Enter new password: Enter it again: postgres=# \q
Server Network Access
The installation configures the server to be available for local connections only. If you need this server to be accessible from other computers in your network follow these:- Ensure the server connection settings (file/etc/postgresql/9.1/main/postgresql.conf):
# - Connection Settings - listen_addresses = '*'
- Allow incoming network connections (file
/etc/postgresql/9.1/main/pg_hba.conf):
# Allow remote connections to any database, # for any user from 192.168.10.0/24 network. host all all 192.168.10.0/24 md5
- Restart server so your changes take place:
/etc/init.d/postgresql restart
Client
pgAdmin III is a database design and management application for use with PostgreSQL (graphical tool). Let install it:apt-get install pgadmin3Try connect to the server you installed with user postgres and password set for database user.
Labels:
debian
,
postgresql
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
How to Renew Certificate with OpenSSL
SSL certificates are valid for certain period of time, usually 365 days. If you are using self signed certificates at some point of time you will need renew them, otherwise services that utilize them "unexpectedly" stop working. That actually greatly depends on client configuration, so if client demand valid server certificate it will not proceed any further.
Suppose your certificate private key (original request) is in file my-key.pem and signed certificate in my-cert.pem.
Suppose your certificate private key (original request) is in file my-key.pem and signed certificate in my-cert.pem.
Validate Certificate
Validate certificate by issuing the following command:openssl verify my-cert.pemHere is a sample output of checking valid cerificate:
my-cert.pem: OKExpired:
my-cert.pem: ... error 10 at 0 depth lookup:certificate has expired OKIf verification of certificate shows it expired, you need renew it.
Renew Certificate
Renewal of expired certificate consists of two steps: revoke old one, sign certificate request.- Revoke expired certificate (you will be asked for Certificate Authority password):
ca1:~/ca# openssl ca -revoke my-cert.pem Using configuration from /usr/lib/ssl/openssl.cnf Enter pass phrase for ./demoCA/private/cakey.pem: Revoking Certificate EFDAF4493BC3D5BB. Data Base Updated
- Rename you certificate key (request) file to newreq.pem.
ca1:~/ca# mv my-key.pem newreq.pem ca1:~/ca# /usr/lib/ssl/misc/CA.sh -sign ... Signed certificate is in newcert.pem
Troubleshooting
If you get error like this one below:failed to update database TXT_DB error number 2You must revoke previous certificate from CA database.
Labels:
openssl
,
troubleshooting
Friday, February 17, 2012
Python Imaging Library Compiled
The compiled Python Imaging Library (version 1.1.7 for python 2.4-2.7 i386 and python 2.7 x86_64) can be found here. See the other post how to get it compiled in Debian.
Thursday, February 16, 2012
How to Install Python Imaging Library in Debian
If you need install Python Imaging Library into virtual environment under Debian you will need set location of several libraries (libfreetype, libjpeg). First of all let setup pre-requirements so we can compile PIL.
You can download pre-compiled version of PIL per this post.
apt-get -y install build-essential python-dev \ python-virtualenv libbz2-dev zlib1g-dev \ libfreetype6-dev libjpeg8-devThe script below simplify PIL configuration/setup procedure.
# Download PIL and uzip it wget http://effbot.org/downloads/Imaging-1.1.7.tar.gz tar xzf Imaging-1.1.7.tar.gz # create virtual environment virtualenv env ARCH=i386 #ARCH=x86_64 cd Imaging-1.1.7 # Set location of libjpeg8-dev sed -e "s,JPEG_ROOT = None,JPEG_ROOT = '/usr/lib/$ARCH-linux-gnu',g" \ setup.py > /tmp/x && mv /tmp/x setup.py # Set location of zlib1g-dev sed -e "s,ZLIB_ROOT = None,ZLIB_ROOT = '/usr/lib/$ARCH-linux-gnu',g" \ setup.py > /tmp/x && mv /tmp/x setup.py # Set location of libfreetype6-dev sed -e "s,FREETYPE_ROOT = None,FREETYPE_ROOT = '/usr/lib/$ARCH-linux-gnu',g" \ setup.py > /tmp/x && mv /tmp/x setup.py # Proceed with installation into virtual environment ../env/bin/python setup.py installThe virtual environment is ready to be used with projects dependent on PIL, e.g. captcha, etc.
You can download pre-compiled version of PIL per this post.
Wednesday, February 15, 2012
How to Revert Broken Package in Debian
You just made upgrade of your Debian testing box and noticed something went wrong, some daemon not starting and you have no idea what to do until the bug will be fixed. Fortunately, you are able to revert broken package in Debian. Here we are going revert broken bind9 package version 1:9.8.1.dfsg.P1-2 and replace it with last known to work.
- We need to find last known to work version of the broken package. Take a look at
/var/log/apt/history.log. You should be able to find information about the package failed to install/configure:
Upgrade: ..., bind9:i386 (9.7.3.dfsg-1+b1, 9.8.1.dfsg.P1-2)...
So here version 9.7.3.dfsg-1+b1 is replaced by 9.8.1.dfsg.P1-2. Thus we found last working version. - Since we know version (9.7.3.dfsg-1+b1) of the bind9 package we can install it from snapshot.debian.org. Go to that site and search for your package. You will get a list of various versions available.
Follow link for with version that you found previously. You will get a list of various options, including source, architecture specific files, etc.
bind9_9.7.3.dfsg-1+b1_i386.deb Seen in debian on 2011-04-20 22:16:02 in /pool/main/b/bind9.
Follow link /pool/main/b/bind9. In my case it was:http://snapshot.debian.org/archive/debian/20110420T221602Z/pool/main/b/bind9/
- Add snapshot url to file /etc/apt/sources.list:
deb http://snapshot.debian.org/archive/debian/20110420T221602Z testing main
- Update your apt repository with the following command:
apt-get -o Acquire::Check-Valid-Until=false update
- Have a look at updated package information:
apt-cache showpkg bind9
You should be able to see something like this:Versions: 1:9.8.1.dfsg.P1-2 ... 1:9.7.3.dfsg-1 ...
1:9.7.3.dfsg-1 is the version we need. - Remove broken package and related dependencies:
apt-get remove bind9 apt-get autoremove
- Install version we need:
apt-get install bind9=1:9.7.3.dfsg-1
Since it complains:The following packages have unmet dependencies: bind9 : Depends: bind9utils (= 1:9.7.3.dfsg-1) but 1:9.8.1.dfsg.P1-2 is to be installed
... let add that one dependency for bind9utils as well.apt-get install bind9=1:9.7.3.dfsg-1 bind9utils=1:9.7.3.dfsg-1
Package pinning
We will use apt pinning feature to prevent packages from being upgraded. Just create a file /etc/apt/preferences.d/bind9 and add the following:
Package: bind9
Pin: version 1:9.7.3*
Pin-Priority: 1001
Package: bind9utils
Pin: version 1:9.7.3*
Pin-Priority: 1001
The next time you run upgrade these two packages remain untouched.
Labels:
apt
,
debian
,
troubleshooting
Subscribe to:
Posts
(
Atom
)